Biden-Harris Administration finalizes ban on ongoing uses of asbestos to protect people from cancer
EPA’s ban is the first rule to be finalized under new Toxic Substance Control Act process, marking historic milestone for nation’s chemical safety efforts
March 18, 2024
Government Agency Press Release – From the United States Environmental Protection Agency
Contact Information – EPA Press Office (press@epa.gov)
WASHINGTON – Today, March 18, 2024, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) announced a final rule to prohibit ongoing uses of chrysotile asbestos, the only known form of asbestos currently used in or imported to the United States. The ban on ongoing uses of asbestos is the first rule to be finalized under the 2016 amendments to the nation’s chemical safety law, the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), which received near-unanimous support in both the U.S. House of Representatives and the Senate.
The action marks a major milestone for chemical safety after more than three decades of inadequate protections and serious delays during the previous administration to implement the 2016 amendments.

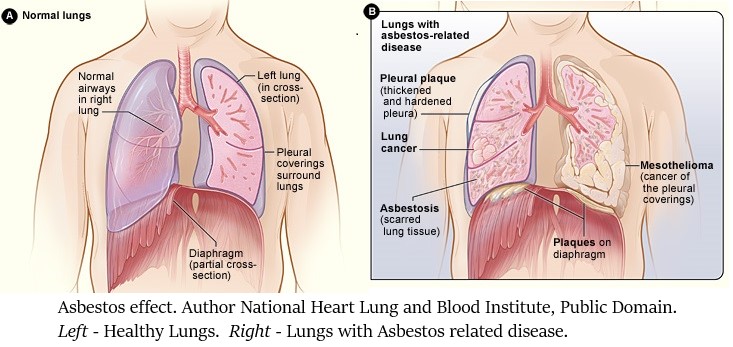
Exposure to asbestos is known to cause lung cancer, mesothelioma, ovarian cancer, and laryngeal cancer, and it is linked to more than 40,000 deaths in the U.S. each year. Ending the ongoing uses advances the goals of President Biden’s Cancer Moonshot, a whole-of-government initiative to end cancer as we know it.
“The science is clear – asbestos is a known carcinogen that has severe impacts on public health. President Biden understands that this concern that has spanned generations and impacted the lives of countless people. That’s why EPA is so proud to finalize this long-needed ban on ongoing uses of asbestos,” said EPA Administrator Michael S. Regan. “Under the President’s leadership, EPA has been working expeditiously to put the nation’s chemical safety program back on track and finally realize the protections of the 2016 law. This action is just the beginning as we work to protect all American families, workers, and communities from toxic chemicals.”
“Asbestos has harmed people across the country for decades, and under President Biden’s leadership, we are taking decisive action to ban its use and advance this administration’s historic environmental justice agenda,” said White House Council on Environmental Quality Chair Brenda Mallory. “This action marks a major step to improve chemical safety after decades of inadequate protections, helping advance President Biden’s Cancer Moonshot goal to end cancer as we know it.”
Chrysotile asbestos is found in products including asbestos diaphragms, sheet gaskets, brake blocks, aftermarket automotive brakes/linings, other vehicle friction products, and other gaskets. The use of asbestos in the United States has been declining for decades, and its use is already banned in over 50 countries.

Although there are several known types of asbestos, the only form known to be imported, processed, or distributed for use in the United States is chrysotile. Raw chrysotile asbestos was imported into the United States as recently as 2022 for use by the chlor-alkali industry. Most consumer products that historically contained chrysotile asbestos have been discontinued.
“Today’s rule is a positive first step to give all Americans a future free of exposure to asbestos – a carcinogen that has killed far too many. This dangerous substance has been banned in more than 50 countries around the world, and the United States is finally starting to catch up.
Above – Chrysotile asbestos – Photo of US Government.
An immediate ban on the import of chrysotile asbestos for the chlor-alkali industry is a long overdue step forward for public health. However, it cannot be the end of the road when it comes to phasing out other dangerous asbestos fibers, and Congress has a role to play here when it comes to providing stronger protections for our health,” said Senator Jeff Merkley.
“It is long past time for the U.S. to ban asbestos, and unacceptable this known carcinogen continues to threaten Americans and devastate families,” said Congresswoman Suzanne Bonamici. “I’ve been spent years advocating for asbestos to be banned and am grateful for the steps the EPA is taking today to finalize its rule to prohibit the import and use of chrysotile asbestos. Banning asbestos will save lives.”
“The Biden Cancer Moonshot is a key pillar of the President’s Unity Agenda. Cancer impacts nearly every American family, and it will take all of us to reach the President and First Lady’s ambitious but achievable goals to prevent more than four million cancer deaths by 2047 and improve the experience of people who are touched by cancer. Banning the use of asbestos will help prevent cancer before it begins—saving and improving American lives across the country,” said Deputy Assistant to the President for the Cancer Moonshot Dr. Danielle Carnival.
“It’s been more than 50 years since EPA first sought to ban some uses of asbestos and we’re closer than ever to finishing the job,” said Environmental Working Group senior vice president Scott Faber. “For too long, polluters have been allowed to make, use, and release toxics like asbestos and PFAS without regard for our health. Thanks to the leadership of the Biden EPA, those days are finally over.”
This public health protection is long overdue. A 1991 court decision that largely struck down EPA’s 1989 ban on asbestos and significantly weakened EPA’s authority under TSCA to address risks to human health from asbestos or from any other existing chemical. The 2016 amendments to TSCA transformed the law with clear requirements and a mandate to comprehensively prioritize and evaluate the risks of chemicals and put in place strong and timely health protections against any unreasonable risks.
EPA has set compliance deadlines to transition away from each use of chrysotile asbestos, which are as soon as is practicable for each use while also providing a reasonable transition period, which the law requires.
Chlor-alkali Sector
The chlor-alkali sector uses asbestos diaphragms to make sodium hydroxide and chlorine, a critical use of which is to disinfect drinking water and wastewater. There are other ways to disinfect water and other ways to produce chlorine; in fact, two-thirds of the chlorine produced in the U.S. is produced without using asbestos. While there are only eight chlor-alkali plants in the United States that still use asbestos diaphragms, EPA must still ensure that the eight facilities have a reasonable transition time for the phase out of asbestos that does not inadvertently adversely impact drinking or wastewater purification efforts.
EPA is banning the import of asbestos for chlor-alkali use immediately to close the door forever on the use of asbestos by this sector. The eight remaining facilities that use asbestos must transition to either non-asbestos diaphragms or to non-asbestos membrane technology, and the final rule ensures that six of the eight will have completed this transition within five years, with the remaining two to follow.
- EPA has determined that converting facilities from using diaphragms that contain asbestos to those that do not within five years provides both a reasonable transition time and is as soon as practicable without disrupting the supply of chlorine that is needed for water purification purposes. EPA also believes that five of the eight facilities likely plan to undergo such conversions.
- EPA has also determined that converting facilities from using diaphragms that contain asbestos to non-asbestos membrane technology requires extensive construction, additional permits, specialized expertise and parts for which there are limited suppliers. EPA has therefore determined that a reasonable transition time for companies that plan to transition multiple facilities to non-asbestos membrane technology is five years to convert their first facility, eight years to convert their second and 12 years to convert their third, and the facilities will be required to certify their continued progress with EPA.
Remaining Uses
The final rule also:
- Bans most sheet gaskets that contain asbestos two years after the effective date of the final rule, with five-year phase-outs for sheet gaskets to be used to produce titanium dioxide and for the processing of nuclear material.
- Allows asbestos-containing sheet gaskets to continue to be used through CY 2037 at the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site to ensure that the safe disposal of nuclear materials can continue on schedule while continuing to protect workers from exposure to radioactive materials.
- Bans the use of asbestos in oilfield brake blocks, aftermarket automotive brakes and linings, other vehicle friction products, and other gaskets six months after the effective date of the final rule.
EPA is requiring strict workplace safety measures to protect workers from asbestos exposure during any phaseout periods longer than two years. EPA is also ensuring that asbestos is disposed of properly, in line with industry standards, Occupational Safety and Health Administration requirements, and the Asbestos National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants. The agency is also requiring recordkeeping.
Separately, EPA is also evaluating other types of asbestos fibers (in addition to legacy uses and associated disposal of chrysotile, and asbestos-containing talc) in part 2 of the asbestos risk evaluation. EPA will release part 2 of the draft risk evaluation soon and will publish the final risk evaluation by Dec. 1, 2024.